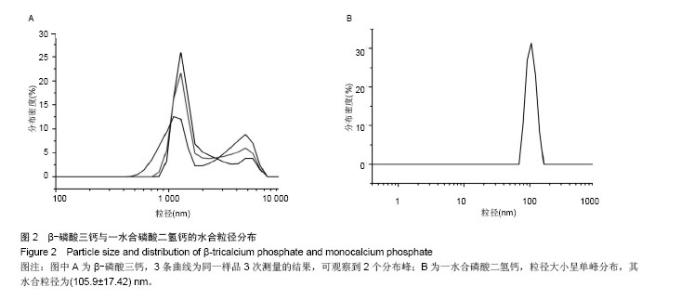
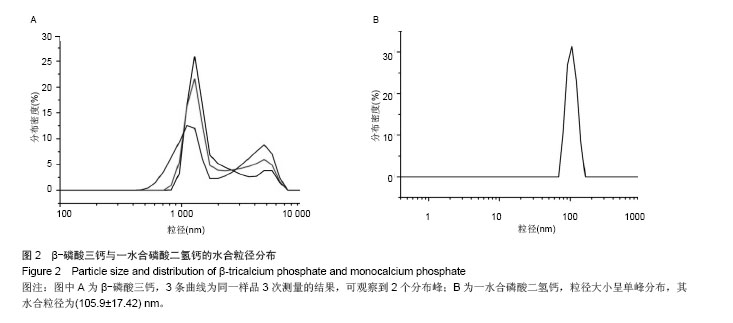
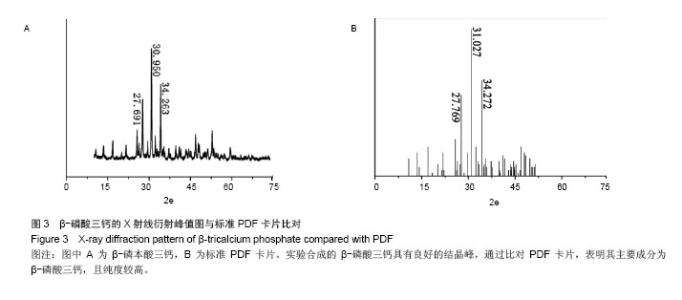
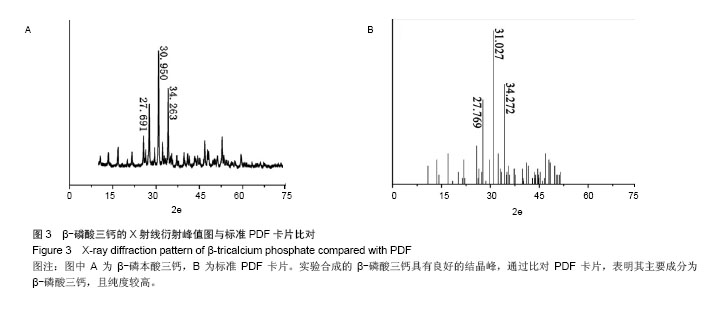
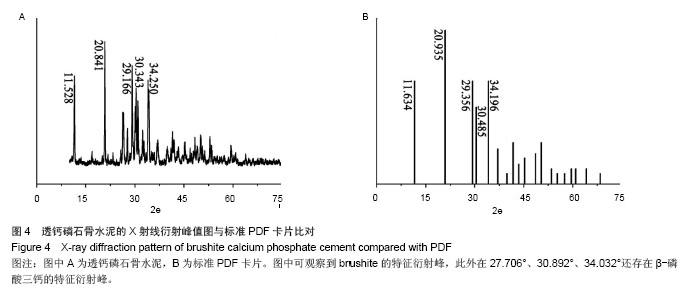
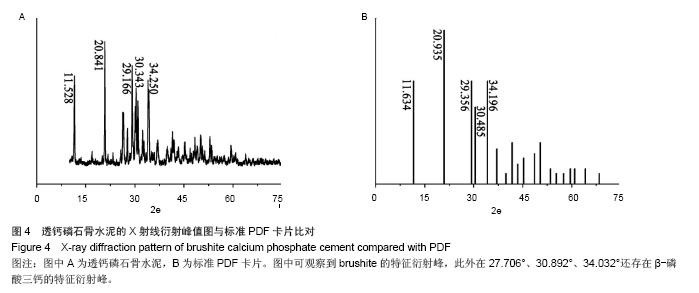
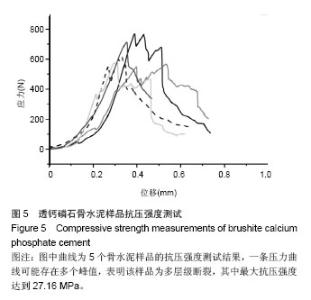
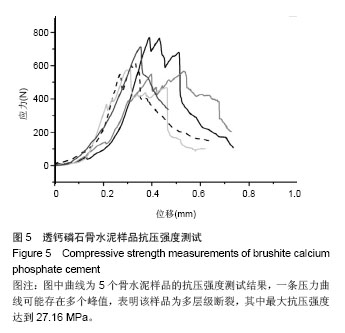
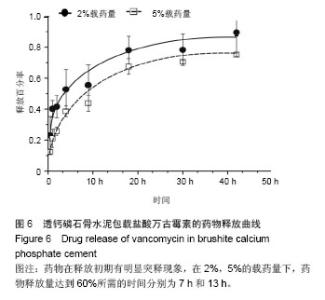
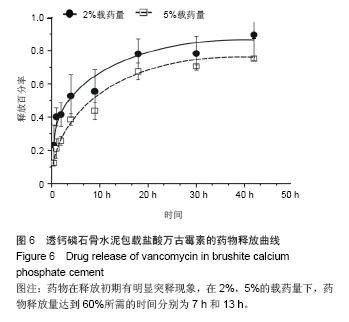
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (3): 427-433.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.03.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation of brushite calcium phosphate cement for controlled drug delivery and its property of drug loading
Yang Di-cheng, Zhong Jian, Liu Tao, Yan Ce, He Dan-nong
- National Engineering Research Center for Nanotechnology (NERCN), Shanghai 200241, China
-
Online:2015-01-15Published:2015-01-15 -
Contact:He Dan-nong, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, National Engineering Research Center for Nanotechnology (NERCN), Shanghai 200241, China -
About author:Yang Di-cheng, National Engineering Research Center for Nanotechnology (NERCN), Shanghai 200241, China -
Supported by:the National High-Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program), No. 2013AA032203; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 51073173; Special Fund for Talents in Minhang District of Shanghai, No. 2012
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Di-cheng, Zhong Jian, Liu Tao, Yan Ce, He Dan-nong . Preparation of brushite calcium phosphate cement for controlled drug delivery and its property of drug loading[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(3): 427-433.
share this article
| [1]Kurashina K,Kurita H,Hirano M,et al. In vivo study of calcium phosphate cements: implantation of an α-tricalcium phosphate/dicalcium phosphate dibasic/tetracalcium phosphate monoxide cement paste. Biomaterials.1997; 18(7): 539-543. [2]Apelt D,Theiss F,El-Warrak AO,et al.In vivo behavior of three different injectable hydraulic calcium phosphate cements. Biomaterials.2004;25(7): 1439-1451. [3]Friedman CD,Costantino PD,Takagi S,et al.BoneSource™ hydroxyapatite cement: a novel biomaterial for craniofacial skeletal tissue engineering and reconstruction.J BiomedMater Res.1998;43(4):428-432. [4]Ooms EM,Wolke J GC,Van de Heuvel MT,et al.Histological evaluation of the bone response to calcium phosphate cement implanted in cortical bone. Biomaterials. 2003; 24(6): 989-1000. [5]Tofighi A,Mounic S,Chakravarthy P,et al.Setting reactions involved in injectable cements based on amorphous calcium phosphate.Key Eng Mater.2000;192:769-772. [6]Constantz BR,Ison IC,Fulmer MT,et al.Skeletal repair by in situ formation of the mineral phase of bone.Science. 1995;267 (5205): 1796-1799. [7]Driessens FCM,Boltong MG,Bermudez O,et al.Effective formulations for the preparation of calcium phosphate bone cements.J Mater Sci Mater Med.1994;5(3):164-170. [8]Ginebra MP,Fernandez E,De Maeyer EAP,et al.Setting reaction and hardening of an apatitic calcium phosphate cement.J Dent Res.1997;76(4):905-912. [9]Mirtchi AA,Lemaître J,Munting E.Calcium phosphate cements: study of the β-tricalcium phosphate-dicalcium phosphate- calcite cements. Biomaterials.1990:11(2):83-88. [10]Lemaitre J,Mirtchi A,Mortier A.Calcium phosphate cements for medical use: state of the art and perspectives of development. Silic Ind.1987;52(9-10):141-146. [11]Bajpai PK,Fuchs CM, McCullum DE. Development of tricalcium phosphate ceramic cements.Quantitative characterization and performance of porous implants for hard tissue applications. Philadelphia, PA: ASTM,1987:377-388. [12]Constantz BR,Barr BM,Ison IC,et al.Histological, chemical, and crystallographic analysis of four calcium phosphate cements in different rabbit osseous sites.J Biomed Mater Res. 1998;43(4):451-461. [13]Apelt D,Theiss F,El-Warrak AO,et al.In vivo behavior of three different injectable hydraulic calcium phosphate cements. Biomaterials.2004;25(7):1439-1451. [14]Ikenaga M,Hardouin P,Lemaitre J,et al.Biomechanical characterization of a biodegradable calcium phosphate hydraulic cement: a comparison with porous biphasic calcium phosphate ceramics.J Biomed Mater Res.1998;40(1):139-144. [15]Barralet JE,Grover LM,Gbureck U.Ionic modification of calcium phosphate cement viscosity. Part II: hypodermic injection and strength improvement of brushite cement. Biomaterials.2004;25(11):2197-2203. [16]Fukase Y1,Eanes ED,Takagi S,et al.Setting reactions and compressive strengths of calcium phosphate cements.J Dent Res.1990;69(12):1852-1856. [17]刘昌胜,陈飞跃,黄粤.原料颗粒对磷酸钙骨水泥水化硬化过程的影响[J]. 硅酸盐学报,1999,27(2):139-147. [18]韩冰,尹玉姬,李宗燕.高性能化磷酸钙骨水泥的研究进展[J].材料科学与工程, 2006,25(5):495-501. [19]Van den Vreken NMF,Pieters IY,Declercq HA,et al. Characterization of calcium phosphate cements modified by addition of amorphous calcium phosphate.Acta Biomaterialia. 2010;6(2):617-625. [20]陶艳,李东旭,李延报.可注射磷酸钙骨水泥的研究进展[J].材料导报A:综述篇,2011,25(2):121-124,31. [21]曹德勇,宋雪峰,陈亦平.骨水泥生物材料研究与开发进展[J].化学工业与工程,2003,20(5):303-309. [22]Ginebra MP,Traykova T,Planell JA.Calcium phosphate cements as bone drug delivery systems: a review.J Controll Release.2006;113(2):102-110. [23]Arkfeld DG,Rubenstein E.Quest for the holy grail to cure arthritis and osteoporosis: emphasis on bone drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Del Rev. 2005; 57(7):939-944. [24]Suzuki T,Arai K,Goto H,et al.The effect of adding cefobid upon the physiochemical properties of calcium phosphate cement dissolution tests for self-setting calcium phosphate cement containing nifedipine.Chen Pharm Bull(Tokyo).2002; 6:741-743. [25]Tahara Y,Ishii Y.Apatite cement containing cis-diamminedichloroplatinum implanted in rabbit femur for sustained release of the anticancer drug and bone formation. J Orthop Sci.2001;6(6):556-565. [26]Joosten U,Joist A,Gosheger G,et al.Effectiveness of hydroxyapatite-vancomycin bone cement in the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus induced chronic osteomyelitis. Biomaterials. 2005;26(25):5251-5258. [27]Legeros RZ.Biodegradation and bioresorption of calcium phosphate ceramics.Clin Mater.1993;14(1):65-88. [28]Bohner M,Lemaitre J,Ring TA. Effects of Sulfate, Pyrophosphate, and Citrate Ions on the Physicochemical Properties of Cements Made of β-Tricalcium Phosphate‐Phosphoric Acid‐Water Mixtures.J Am Ceram Soc.1996; 79(6):1427-1434. [29]Engstrand J,Persson C,Engqvist H.The effect of composition on mechanical properties of brushite cements.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2014;29:81-90. [30]Tamimi F,Sheikh Z,Barralet J.Dicalcium phosphate cements: Brushite and monetite.Acta Biomaterialia.2012;8(2):474-487. [31]田金花,杨华,迟光伟,等.壳聚糖和壳寡糖的磷酸化研究[J].化学研究与应用,2010,22(5):554-558. [32]Anirban JM,Thai VV,Min YK,et al.In vitro bioactivity and biocompatibility of calcium phosphate cements using Hydroxy-propyl-methyl-Cellulose (HPMC). Appli Surf Sci. 2010;257:1533-1539. [33]Bigi A,Torricelli P,Fini M,et al.A biomimetic gelatin-calcium phosphate bone cement.Int J Artif Organs.2004;27(8): 664-673. |
| [1] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [2] | Ma Jinchao, Liu Tiansheng, Liu Aipeng, Wang Hao, Wang Qi, Liang Yongjian, Wang Lin, Di Haiwei. Photodynamic antimicrobial chemotherapy for repairing a rabbit model of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1254-1259. |
| [3] | Wang Xuefeng, Shang Xifu . Curative effects of three filling materials in the treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 863-869. |
| [4] | Liu Dan, Min Changqin, Lu Shuai, Chen Yue, Sun Yong. Osseointegration induced by beta-tricalcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet-rich fibrin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 888-893. |
| [5] | Xiang Bingyan, Li Peng, Bo Fan, Zhou Sirui . Repair of bone defects due to chronic osteomyelitis in rabbits using nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan scaffold carrying vancomycin/polyactic-co-glycolic acid sustained-release microspheres combined with autologous red bone marrow [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 843-848. |
| [6] | Cheng Jian, Zhang Jun, Guan Jie, Zeng Junkai, Zhao Xin, Xie Youzhuan. Silver nanoparticle-doped tricalcium phosphate: in vitro and in vivo toxicity in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 917-923. |
| [7] | Xie Wenjia, Wang Jian, Pei Xibo . Applications of single cell nanoencapsulation: single cell catalysis, cell protection and treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 278-283. |
| [8] | Cui Tingting, Qiu Zewen, Gui Lin, Zhong Weijian, Ma Guowu. Effect of gelatin sponge/beta-tricalcium phosphate composite with different doses of basic fibroblast growth factor on bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 190-195. |
| [9] | Gao Shan, Zhou Fang, Lü Yang, Yuan Liang, Li Ailing, Qiu Dong. Preparation and characterization of novel porous polymethyl methacrylate bone cements [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 204-210. |
| [10] | Liu Yazhen, Qiu Xiaoming, Li Songkai. Orthogonal optimization of vancomycin/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres: preparation and drug release in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 211-217. |
| [11] | Peng Chenjian, Du Bin, Sun Guangquan, Liu Xin, Xue Peng, Cao Liangquan. Three-dimensional printing beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold loaded with icariin particles for repairing osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2162-2168. |
| [12] | Li Haoliang, Wang Xibin, Zuo Ruiting. Calcium phosphate cement/fibrin glue composite loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 promotes osteoporotic fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2156-2161. |
| [13] | Chen Yue, Zhang Tianke, Xu Yong. Nanomaterials applied in tumor imaging diagnosis and treatment: an integration tendency [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2241-2247. |
| [14] | Zhang Xiaodong, Liu Ying. Patent analysis for calcium phosphate bone cements [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2269-2278. |
| [15] | Zheng Rui, Xie Jing, Lu Shuai, Sun Yong. Beta-tricalcium phosphate combined with advanced platelet-rich fibrin contributes to bone regeneration: X-ray and immunohistochemical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(10): 1514-1519. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||